Earthing or grounding is the process of transferring the immediate discharge of electrical energy directly to the Earth with the help of the low-resistance wire. The electrical earthing is carried out by connecting the non-current-carrying part of the equipment or the neutral part of the supply system to the ground.
Think of all the appliances in your home that run on electricity. The usual suspects would be refrigerators, air conditioning units, washing machines, televisions, laptops and water heaters. Have you ever wondered why the plugs that go in the wall sockets have 3 pins instead of 2?
The refrigerator in your kitchen is a made of metal, with metal components and a metal frame. Logically speaking, one should be electrocuted the moment any contact is made with a refrigerator, since metals are such great conductors of electricity.

Yet that obviously doesn’t happen because the components are insulated. Why don’t we get zapped if the insulation fails and electricity begins to leak out of the refrigerator’s chassis? Ever speculated on that potential time bomb in your kitchen?
The answer to these questions lie in the terms “Earthing” or “Grounding”.
What Is Earthing Or Grounding?
A safety measure devised to prevent people from getting shocked if the insulation inside electrical devices fails is called Earthing. To answer our initial question, the third pin in the plug is actually the “Earth” or “Ground” connection of the electrical appliance.
The Earth, being a good conductor of electricity, acts as a convenient path for the flow of electrons that escape the insulation. Furthermore, the gigantic size of the Earth paves a path for the safe discharge of the electric charge.
In technical terms, Electrical Earthing can be defined as the process of transferring the immediate discharge of the electrical energy directly to the Earth with the help of the low-resistance wire. The electrical earthing is carried out by connecting the non-current-carrying part of the equipment or the neutral part of the supply system to the ground.
As stated earlier, earthing provides a simple path for the leakage current i.e., the current that escapes from a device if there’s any fault in the insulation. The short circuit current (current that follows the path of least resistance) of the equipment passes to the Earth, which has zero potential, thus protecting the system and equipment from damage.
Also Read: What Determines When An Appliance Needs A 3-Pronged Plug With A Ground Vs A 2-Prong Plug-In?
Why Is Earthing/Grounding Necessary?
There are 3 mains reasons why all electric devices need to be connected to the Earth.
Human Safety
A properly earthed device doesn’t leak out any current. This prevents humans from getting shocked if any internal faults in the device occur.

Safety Of Electrical Equipment
Earthing provides stability to electronic equipment. It prevents over-current or excessive voltage in appliances. Over-voltage can cause the device to spontaneously combust due to overheating, so technically, earthing is also a fire prevention measure.
Protection Of Buildings From Lightning
It is interesting to note that, apart from electrical appliances, large structures such as skyscrapers are also earthed. The earthing device is in the form of lightning arrestors, which are placed at the highest point of the building and connected to the ground via a conducting wire or plate. In the scenario when lightning strikes a building, the copper lightning arrestor draws in the jolts of lightning and transfers that massive amount of energy to the ground, thus preventing any damage to the structure or harm to its occupants.

How Earthing Came Into Existence?
Electrical devices weren’t always grounded. Humans first began using electricity in their homes in the 19th century. Initially, we weren’t aware of the potential dangers of current when it comes in contact with the human body.
Between 1880 and 1920, the transmission and distribution of electrical power were carried out via unearthed neutral connections. The supply lines were uninsulated and placed out of reach so that humans wouldn’t come in contact with them. Homes were supplied with 110 V AC. It was a massive recipe for disaster. During this period, many people had to endure electric shocks and rampant blown fuses.
In 1923, France made it mandatory for motors with ratings of higher than 150 V to have insulated chassis and a proper earthing system in place. Thus, for a generation of “shocked” people who had endured atrocities from their electrical appliances, a new era had dawned. With earthing norms in place, better days were ahead.
Also Read: How Does Electricity Kill?
Types Of Earthing Methods
The following types of earthing systems are used to connect electrical systems to the earth.
Plate Earthing
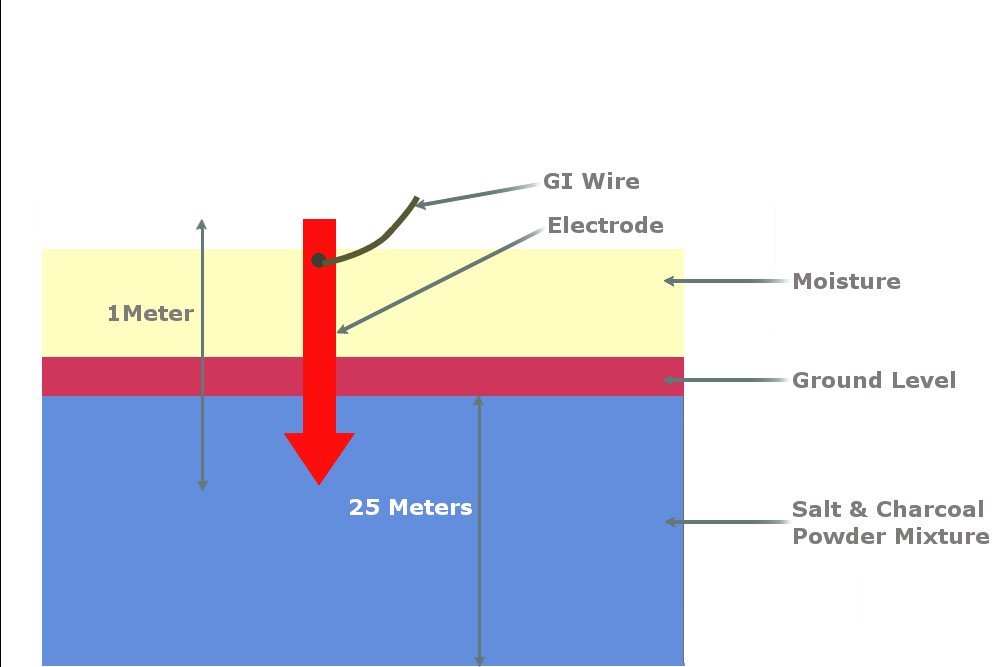
Plate earthing employs a copper or galvanized iron that is buried vertically into the earth in a pit. This pit is more than 10 feet deep. These earth pits are then alternately filled with charcoal and salt layers.
Pipe Earthing
A galvanized steel pipe is placed in the soil. The pipe is drilled with holes for connecting the earthing wires. The length and diameter of the pipe depend on the type of soil and electrical installation.

Similar to plate earthing, pipe earthing also uses a mixture of salt and charcoal. This is the most commonly used earthing method.
Rod Earthing
This is almost identical to pipe earthing, as it requires the burying of a rod made of copper or galvanized iron. The rods are in the form of electrodes, which are embedded in the soil, thus decreasing the resistance of the earth as required.
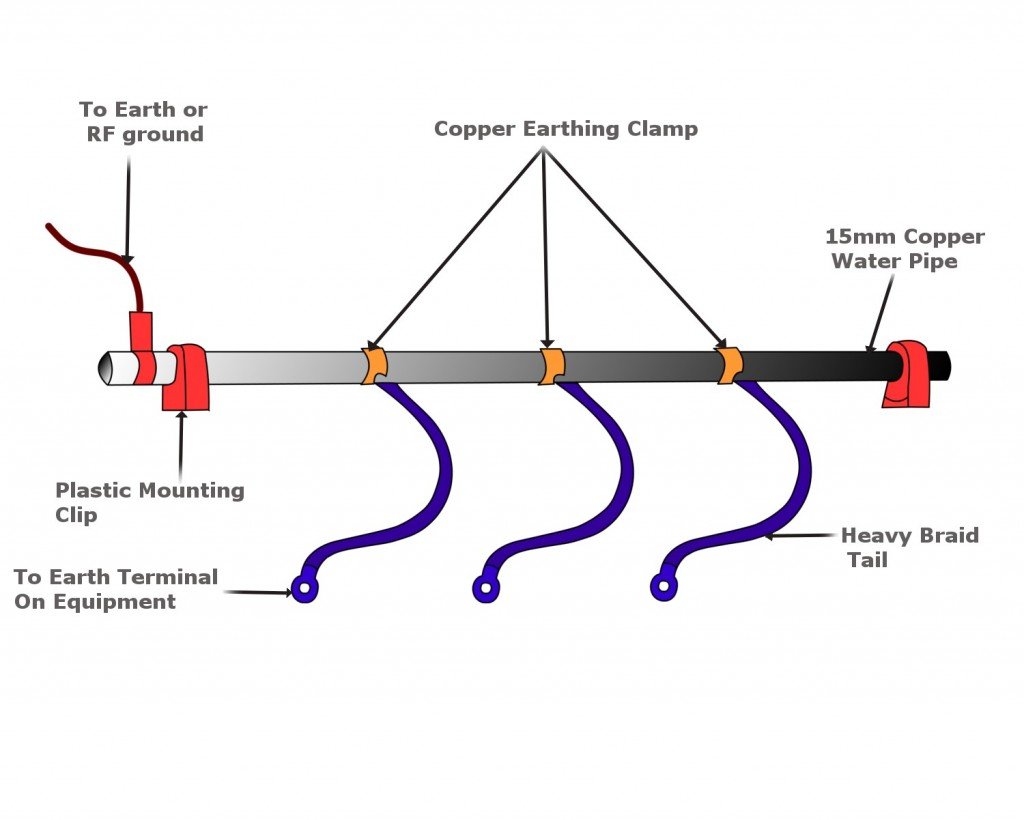
Water Main Method
This method uses water mains, i.e., galvanized GI pipes. These pipes are buried in the earth and clamped using earthing clamps, which minimize the resistance of the electrical connection.
What Factors Affect Earthing Installations?
Several elements need to be considered before carrying out earthing installations.
The type of soil is crucial for calculating the effectiveness of the earthing. Earth’s resistance, moisture level in the soil, salts in the soil, etc. will also play a significant role in determining the way the earthing is made.
Another major factor is the composition of the soil. For example, rocky soil must be treated very differently than wet soil.
Apart from the soil, the location of the earth pit is important to determine how the installation should be completed. If there are underground obstructions in the form of rock beds, then they will affect the installations.
To those who have never been stung by the wrath of excited electrons, you know who to thank. Mother Earth with her zero potential has probably kept you alive more times than you can count!
How well do you understand the article above!

References (click to expand)
- https://download.schneider-electric.com/files?p_enDocType=Cahier+Technique&p_File_Name=ECT173.pdf&p_Doc_Ref=ECT173
- Sundaravaradan, N. A., & Reddy, M. J. B. (2018, March). How Is Earthing Done?. IEEE Potentials. Institute of Electrical and Electronics Engineers (IEEE).
- Electrical Earthing - Methods and Types of Earthing & Grounding. electricaltechnology.org
