Table of Contents (click to expand)
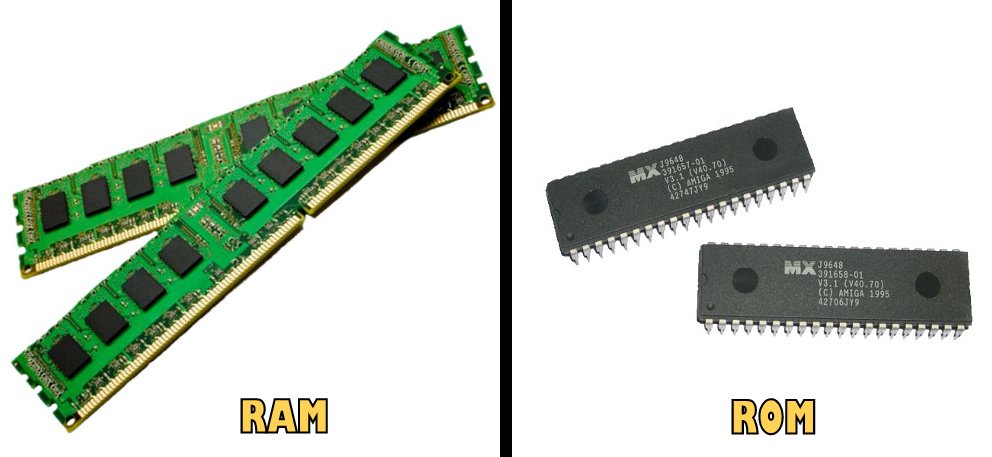
RAM is a type of computer memory that stores data that is currently being used so that the processor can access it quickly. ROM is a type of computer memory that stores data that has been pre-recorded.
The differences between ROM (Read Only Memory) and RAM (Random Access Memory) are:
- ROM is a form of permanent storage, while RAM is a form of temporary storage.
- ROM is non-volatile memory, while RAM is volatile memory.
- ROM can hold data even without electricity, while RAM needs electricity to hold data.
If you’re not an alien reading this from a galaxy far, far away, then you have probably heard these terms countless times—RAM and ROM. That being said, RAM is more commonly encountered by the common person. You certainly would have learned about them in your computer class, or perhaps you recognize the terms and at least know they are related to computer memories. However, there’s a fair amount of the populace that can’t really distinguish between RAM and ROM and wouldn’t be able to explain how they function differently!
As always, let’s brush away the cobwebs surrounding these common and useful tech terms.
What Is RAM?
Random access memory, often abbreviated as RAM, is a hardware element of a computer where programs, operating systems, and data that are currently being used is stored so that the processor can retrieve it quickly.
Think of RAM as a memory bank for the computer. The amount of multi-tasking you can do and the games you can play on the computer or phone depend heavily on the amount of RAM available, in addition to the prowess of the processor. The data on RAM is volatile, meaning that whenever you power off the device, the data would be erased. It is a high-performing expensive memory component that is used to store data about the programs being run in real-time.
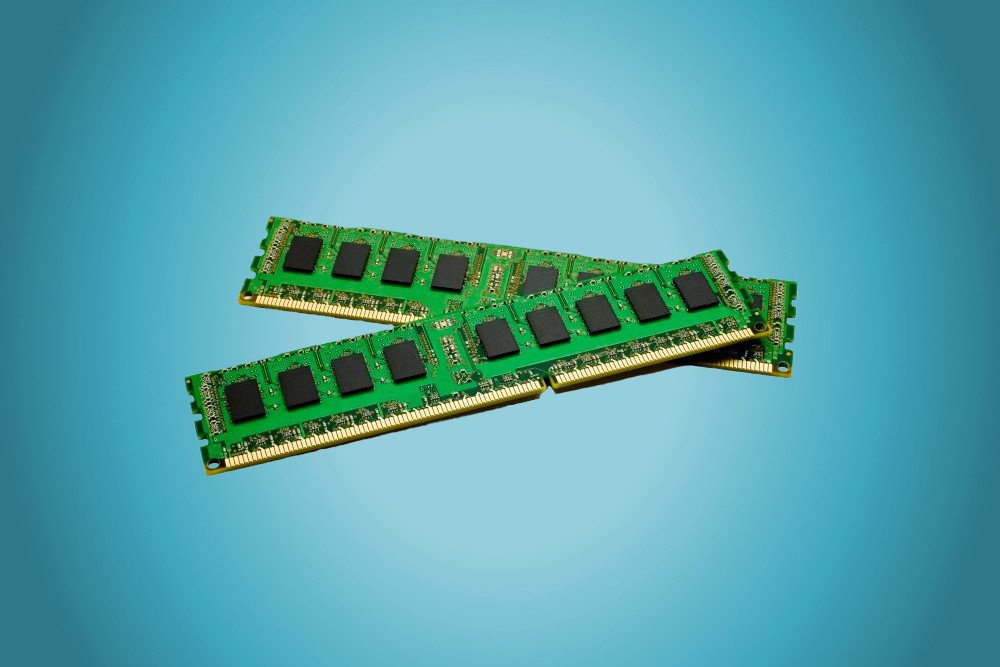
If you ever open up your computer cabinet (computer tower), you will find one (or two) oblong chips installed in a slot on the motherboard. That’s the RAM. These days, motherboards come with more than one RAM slot, which gives you the flexibility to increase your RAM capacity, enabling better operational speed and computational performance. Now, let’s look at two main types of RAM available in the market.
Types Of RAM
- SRAM: Static random access memory (SRAM) is a type of RAM that stores data using a 6-transistor memory cell. SRAM is generally used as a cache memory for processors. It is generally not replaceable by the end user.
- DRAM: Dynamic random access memory (DRAM) is a type of RAM that stores data using a pair of transistors and capacitors. DRAM is comparatively cheaper than SRAM, but the operating speed is slow. Their replaceability makes them suitable for computer systems whose memory modules can be replaced/upgraded.
Also Read: How Does Computer Memory Work When It’s Switched Off?
What Is ROM?
ROM, on the other hand, is a type of memory where data has been pre-recorded. It contains the programming that helps a computer or smartphone ‘boot up’.
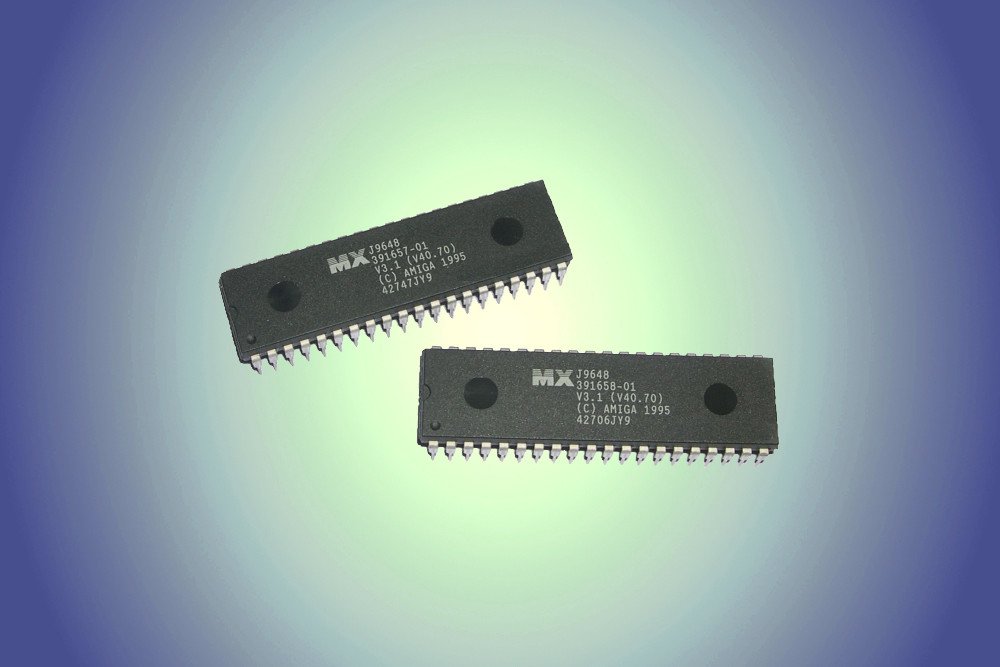
Commonly referred to as Read Only Memory, ROM retains its contents even after the computer is turned off; that’s why a computer can be switched on in the first place. It’s fair to say that if it weren’t for ROM, you wouldn’t ever be able to fire up your computer.
When it comes to smartphones, ROM is generally referred to as the internal storage capacity. It is technically called eMMC which stands for embedded multi-media card. This memory is usually soldered onto the main circuit board of the smartphones and cannot be replaced.
Let’s look at 3 main types of ROM.
Types Of ROM
- PROM: Programmable Read Only Memory (PROM) is a blank version of ROM that can be written/modified just once. Using a PROM, a computer geek can program it once with the help of a special tool called a programmer, wherein he burns a specific program into the memory that cannot then be rewritten.
- EPROM: Erasable Programmable Read Only Memory (EPROM), unlike PROM, allows for writing and rewriting several times. However, to erase the previously stored data, ultraviolet (UV) rays are required. EPROM chips come with a quartz window. Whenever UV light of a specific frequency is passed through, it burns the previously stored data and thus empties it to be filled with another program. EPROMs have low durability and wear out over time. They generally have a lifetime of 1000 erasures.
- EEPROM: Electrically Erasable Programmable Read Only Memory (EEPROM) is the most sophisticated type of ROM that not only allows rewriting of the program several thousand times, but does this without needing dedicated equipment and conditioning like EPROM. Unlike the two other forms of ROM, the EEPROM allows the programmer to write and rewrite programs onto it without needing special equipment or even needing to disassemble the ROM card from the main system.
So far, we have discussed the definitions, working, and types of RAM and ROM memories. However, since both of them are types of memories, and often sound somewhat similar, people generally confuse the two.
With that in mind, let’s look at some of the key differences between RAM and ROM.
Also Read: Where Do Deleted Files Go In A Computer?
ROM Vs RAM
Data Retention
This is the most noteworthy difference between these two forms of memory. ROM is a form of non-volatile memory, which means that it retains information even when the computer is shut down. RAM, on the other hand, is considered a volatile memory, only holding data for as long as the computer is up and running. After that…

Physical Appearance
RAM is a thin rectangular chip that you can find inserted in a slot on the motherboard, whereas ROM is typically an optical drive made of magnetic tapes. Furthermore, RAM is usually bigger than ROM.
Storage Capacity
When it comes to computers, a ROM chip usually stores few megabytes of data (4 MB ROM is quite common these days). In contrast, a RAM chip can store much more, measured in gigabytes. For reference, 1 gigabyte is 1024 megabytes. High-end computers these days come with RAM of 16 GB or even 32 GB.
Speed
RAM trumps ROM in terms of speed; it accesses data much faster than ROM and boosts the processing speed of the computer. In terms of storage read speeds, ROM does this at a rate of a few MBs/second, whereas the read speed of RAM is a few GBs/second. In a head-to-head comparison, RAM is several hundred times quicker than ROM.
Ease Of Writing Data
It’s easier to write data in RAM than in ROM, since the latter is a place for storing very limited, albeit immensely important and permanent information. As we have seen earlier, except in the case of EEPROM, it’s generally very difficult to alter data in a ROM memory.
Let’s make the relative difference between RAM and ROM a bit more clear for you to discern between the two:
| Parameter | RAM | ROM |
| Volatility | Volatile | Non-volatile |
| Physical chip size | Bigger | Smaller |
| Storage capacity | Higher | Lower |
| Speed | Faster | Slower |
| Cost | Expensive | Cheaper |
| Data retention | Cannot hold data without power | Can hold data without power |
| Usage | Primary memory modules, cache | Firmware, RFID tags |
The next time you find yourself in a circle of computer geeks, make sure that you bring this information to the table. They might already be aware of it, but they’ll certainly be impressed!
Test how well you understand the difference between RAM and ROM

