Table of Contents (click to expand)
Metals are good conductors of heat and electricity because they contain a glut of free electrons. These free electrons are able to move around freely and collide with one another, propagating heat and electricity through the metal.
The majority of materials that conduct heat and electricity are metals, for the simple reason that metals contain a glut of free electrons.
What Are Free Electrons?
Although electrons don’t actually inhabit atoms like the planets inhabit the solar system, the atomic model based on the solar system model, in which the electrons in an atom revolve around the nucleus like the planets revolve around the sun, does provide a simpler, layman explanation for complex or esoteric quantum mechanical phenomena.
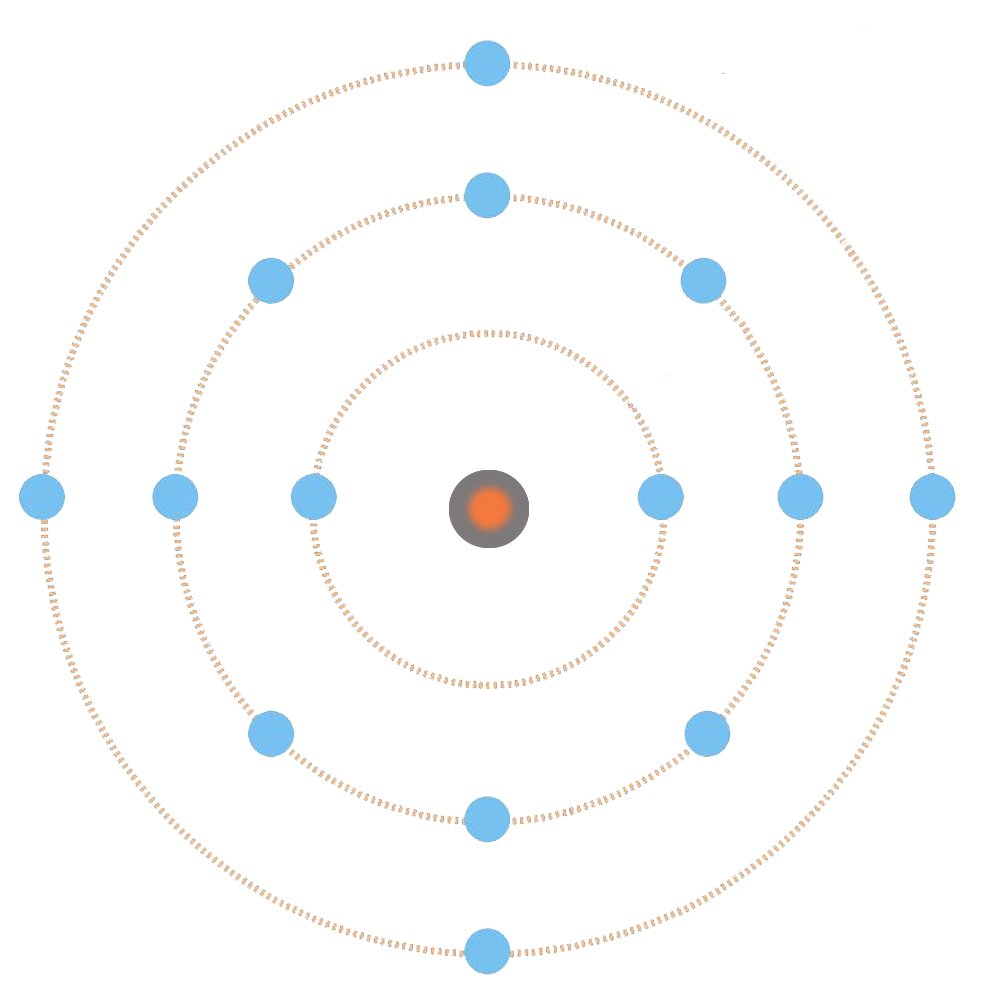
It is obvious and universally known that it is the positive nucleus that binds the negative electrons to the atom. The force with which this is achieved is called the Coulomb force. However, the force becomes weaker with distance: one can infer from this model that, as the shells increase, the force pulling the electrons occupying them becomes increasingly weaker, and weakest, obviously, when pulling the electrons into the outermost, or what is called the valence shell.
These electrons are pulled so weakly that they manage to escape and free themselves from the atom. They are therefore referred to as free electrons. What is responsible for a metal’s propensity to lose its valence electrons is its large atomic size and its own paucity of valence electrons. Non-metals, such as chlorine, possess seven valence electrons, a feature that has forced nature to make its atom smaller and therefore easier for its nucleus to hold them. On the other hand, metals have at most three valence electrons; nature isn’t indulgent enough to make an atom smaller to hold only three electrons, as this would her require to spend excess energy.
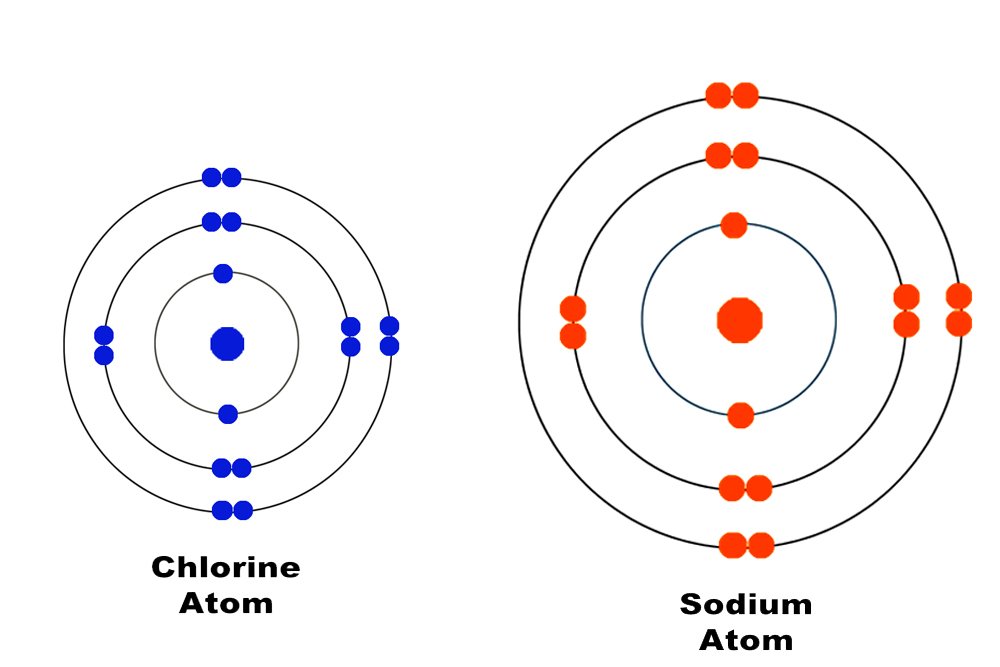
Bear in mind that each metal atom produces one or two free electrons, and a sheet of any metal contains at least a billion billion atoms. The sheet is therefore absolutely teeming with free electrons, and it is these free electrons that propagate the heat and electricity passing through it.
Also Read: How To Find The Number Of Valence Electrons In An Element?
How Free Electrons Propagate Electricity And Heat
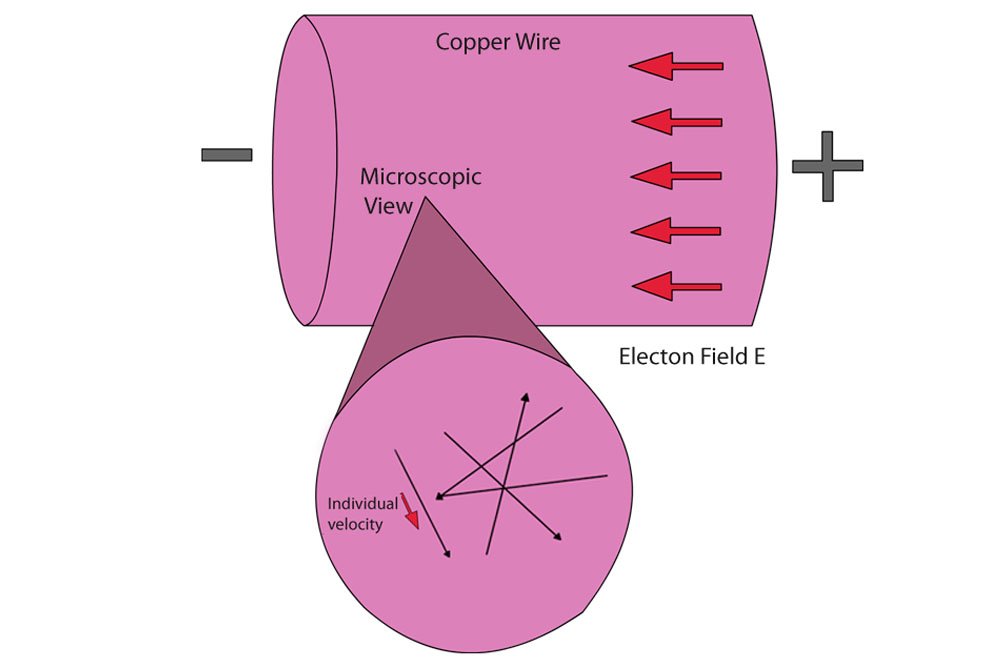
When we connect a copper wire to a battery, the positive terminal attracts the negative free electrons towards it. The sudden force exerted by the electric field causes them to go haywire and vigorously collide with each other at tremendous velocities. What ensues is a domino effect: the free electron into which the free electron behind it collided is impelled forward only to collide with a free electron in front of it, which is then impelled to collide into another free electron and so on until the last free electron in the queue is impelled into the circuit. However, on average, the electrons move forward with a relatively tiny velocity called the drift velocity. Panoramically, one would see a dense river of free electrons coursing towards the positive terminal, and what is current but the flow of electrons?
Heat is mediated through a metal in a similar way. A source of heat energy is nothing but a source of kinetic energy. When we bring a source of heat towards a material, it imparts kinetic energy into the material’s atoms. This kinetic energy causes the atoms to vigorously jiggle in their place. The greater the heat, the greater the intensity of the jiggling.
Ionic compounds also conduct heat as the ions jiggle in their positions. However, ionic compounds are characterized by a highly symmetrical geometric arrangement or structure. They jiggle, but their movement is dramatically restrained by this structure. Pure metals, on the other hand, are superlative conductors because, although their atoms are restrained by structure, their electrons are not… they’re free! The electrons are unrestrained and therefore begin to move around haphazardly when the source imparts kinetic energy into them. They then collide into neighboring electrons, thereby transferring their kinetic energy. The collisions emulate a domino effect and heat is propagated from the hot region, the region closer to the source, to the cold region, the far end of the metal.
I say pure metal because alloys are relatively poor conductors of heat and electricity. This is because alloys are formed by introducing foreign atoms into a metal. This leads to an increase in irregularities, which then obstruct the motion of a free electron. As the free electrons are unable to travel and collide into one another, heat and electricity become more difficult to propagate.

The introduction of foreign atoms is always a point of debate because, while it reduces conductivity, it also improves the metal’s other properties, such as strength. Iron rusts, while stainless steel, an alloy of iron and chromium, does not. As it is the free electrons that are responsible for both — a metal’s ability to conduct electricity and its ability to conduct heat, it’s no coincidence that the laws governing the conduction of electricity are very similar to the laws that govern the conduction of heat.
Also Read: Why Is Rust A Poor Conductor Of Electricity?
How well do you understand the article above!

