Table of Contents (click to expand)
Some common physical effects of taking performance-enhancing drugs include increased muscle mass, increased strength, increased endurance, and decreased fatigue. However, these drugs can also lead to a number of negative side effects, such as baldness, infertility, shrunken testicles, increased aggressiveness, anxiety attacks, and hypertension.
Tyson Gay, an American sprinter who regularly competes in the 100- and 200-meter dash, holds the record as the second-fastest athlete in history, right behind Usain Bolt – a title that he acquired when he darted through 100 meters in just 9.69 seconds! He has won numerous medals in a number of international competitions, including a silver medal in the 2012 Summer Olympics held in London.
However, one incident dealt a nasty blow to his public image: in May of 2013, he tested positive for an anabolic steroid – a banned substance in sporting events. Following that, he was suspended for a set amount of time and stripped of his silver medal by the United States Anti-Doping Agency (USADA).
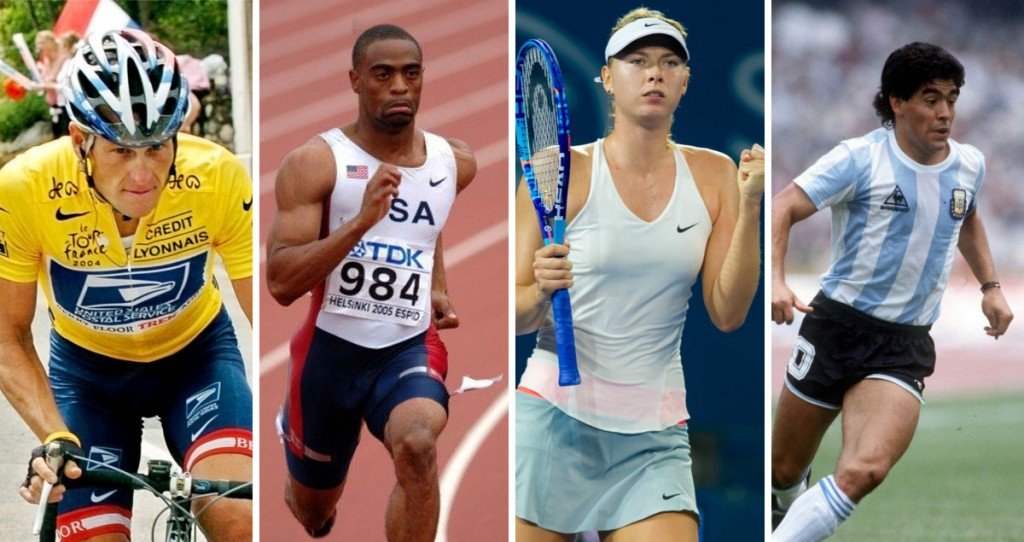

There have been numerous instances throughout sporting history when athletes have tested positive for a prohibited substance and have subsequently been suspended from participating in that sport in the future. The question is – what do these pills/drugs do to athletes’ bodies that makes them perform so exceptionally for that short time? What’s so special about these drugs that makes athletes risk their entire career, legacy and public image in return for outstanding performance?
What Are Performance-Enhancing Drugs?
As the name clearly indicates, Performance-Enhancing Drugs or PEDs are substances that are widely known to increase certain bodily features (e.g., strength, power, endurance etc.) of the user, resulting in a significant improvement in his/her athletic performance. Any substance that augments a subject’s physical activity or affects their arousal level and perception of pain and related sensations is considered a performance-enhancing drug (PED).
The practice of using PEDs (more specifically known as ergogenic aids in an athletic context) in sporting events is commonly known as doping, and is strictly prohibited throughout the world for obvious reasons. Anabolic agents, peptide hormones, diuretics and masking agents are just some of the many drugs banned by the USADA.
Although these drugs are most commonly associated with athletes and bodybuilders, military personnel and students (to improve their cognitive performance) also use them to enhance their performance in various fields.
Also Read: Why Are Xenon And Argon Banned In Sports?
How Do Performance-enhancing Drugs Affect Athlete Performance?
There are various types of drugs that affect a wide range of bodily features and functions for a short period of time. Therefore, the choice of a PED by an athlete totally depends on the type of sport they play. Here are a few commonly used types of PEDs:
Anabolic Agents And Steroids
This is the most commonly used and therefore most notorious category of PEDs. Anabolic drugs give a boost to the levels of testosterone produced by the body, which greatly helps in building muscle, gaining strength and helping heal the damage to muscles that occurs during workout sessions. Anabolic agents also help the subject be more aggressive in general, which is seen as a good thing in certain sporting events.

On the flip side, using too many anabolic agents can lead to a number of nasty side effects, including baldness, infertility, shrunken testicles etc. Some well-known anabolic drugs are stanozolol, clenbuterol, Androstenedione etc.
Human Growth Hormone (HGH)
Growth hormone is produced naturally by the pituitary gland, a pea-sized organ attached to the base of the brain, but the production of growth hormone does decline with age. When taken as a drug, it boosts speed and strength in the short term, which makes it another notorious PED in the sporting world.

Stimulants
These drugs enhance the focus and situational alertness of the subject. Amphetamines, ephedrine and methylphenidate – all of which are popular stimulants among athletes – are known to stimulate the central nervous system, increase reaction time, and enhance hand-eye coordination, focus and alertness on the field. These advantages come in pretty handy in certain sports (like football).
Ergogenic Aids
Also known as athletic performance-enhancing substances, this category of PEDs includes a number of drugs that have varied short-term effects on the body, including decreased fatigue and perceived exertion, an increase in high-intensity exercise capacity, and other effects that significantly boost one’s athletic performance. Amphetamine, methylphenidate and creatine are some examples of this category of PEDs.

Nootropics
People generally tend to associate PEDs with athletes and bodybuilders, but there is a class of PEDs that stands out in this regard. Nootropics, also known as ‘cognition enhancers’, temporarily affect certain cognitive features of subjects, such as memory, attention control, attention span and concentration, so they are commonly used by students and academicians.

There are a few other categories of PEDs, such as sedatives and anxiolytics, adaptogens, blood boosters and so on, and there is also a long list of drugs that fall under one of these categories, making their use prohibited before a sporting event.
Also Read: Are Athletes Really Getting Faster, Taller And Stronger?
The Negative Effects Of PEDs
Although PEDs have a decidedly advantageous impact on a subject’s body and performance in the short term, the side effects are devastating in the long run, both physically and psychologically. Baldness, impotence, breast tissue development, reduction in sperm production, hypertension, anemia, severe headaches, increased aggressiveness leading to criminal behavior, and anxiety attacks are just some of the countless negative effects of using PEDs.
Apart from being incredibly harmful to users both physically and mentally, the use of PEDs is also highly unethical. By artificially enhancing one’s performance through illegitimate means, one not only registers an unlawful win, but also robs honest, hardworking athletes of their chance to win.
How well do you understand the article above!

References (click to expand)
- Doping in sport - Wikipedia. Wikipedia
- Exploring Topics in Sports: Why Do Athletes Risk Using Performance Enhancing Drugs? - sps.northwestern.edu:80
- Performance Enhancing Drugs: History, Medical Effects & Policy. Harvard University
- Effects of Performance-Enhancing Drugs | USADA. The United States Anti-Doping Agency
- Performance-enhancing drugs: Know the risks - Mayo Clinic. The Mayo Clinic
- Kaur, J., Masaun, M., & Bhatia, M. S. (2014). Performance Enhancing Drug Abuse in Athletes and Role of Physiotherapy. Delhi Psychiatry Journal, 17(2), 413-418.
