Table of Contents (click to expand)
The glue doesn’t stick to the inside of the bottle because it needs air or water vapor to set and strongly adhere to another object. There are also some other kinds of glue that stick to objects as the result of chemical reactions. Since there is a very small amount of air present inside the glue bottle, the glue simply doesn’t have access to enough air, so it doesn’t adhere to the inside of the bottle.
Glue normally doesn’t stick to the inside of the bottle because it needs air or water vapor to set and strongly adhere to another object. There are also some other kinds of glue that stick to objects as the result of chemical reactions. Since there is a very small amount of air present inside the glue bottle, the glue simply doesn’t have access to enough air, so it doesn’t adhere to the inside of the bottle.
We use glue all the time to stick things together. I just love the basic idea of glue; it mends objects and puts broken stuff back together. However, strangely enough, glue, which has the ability to stick to (most) objects, doesn’t stick to the tube/bottle/container in which it’s packed. Since it adheres to objects so readily, it would make sense for it to stick to the inner lining of the tube, but in reality, we all know that that doesn’t happen.
Why is that?

Different Kinds Of Glue
It’s important to note that glue comes in many kinds; you may be familiar with a few, but not necessarily all of them. The regular white glue that most of us know so well is made of a host of chemicals known as polymers.
This is the most common type of glue and can be used for many porous and semi-porous materials, such as paper, wood, cardboard, cloth and so on.
Yellow glue, commonly sold under the brand name Titebond, is an aliphatic resin (AR) glue. It’s creamier and thicker than white glue and works very well with both porous and semi-porous materials, especially wooden surfaces.

Then there are certain other adhesives too, such as hide glue, polyurethane glue (Gorilla glue), epoxy and cyanoacrylate (super glue). Some of these require air to set, while others go through chemical changes to achieve their tight grip, but none of these glues stick to the inside of their bottles.
Also Read: How Is Glue Made?
Glue Doesn’t Stick To The Bottle It’s In
Glues are obviously designed to work after they leave their container, not before. Different types of glue achieve this in various ways: some adhesives have solvents that keep them in liquid form and non-sticky within the bottle.
Take white glue, for instance. It has water as the solvent, which keeps it in a thick, liquid form. However, when the glue is squeezed out of the tube band applied to a surface, it comes in contact with the surrounding air. As a result, the water present in the white glue evaporates, making it harden. What you are left with are sticky polymers that hold objects together. This is called mechanical adhesion.
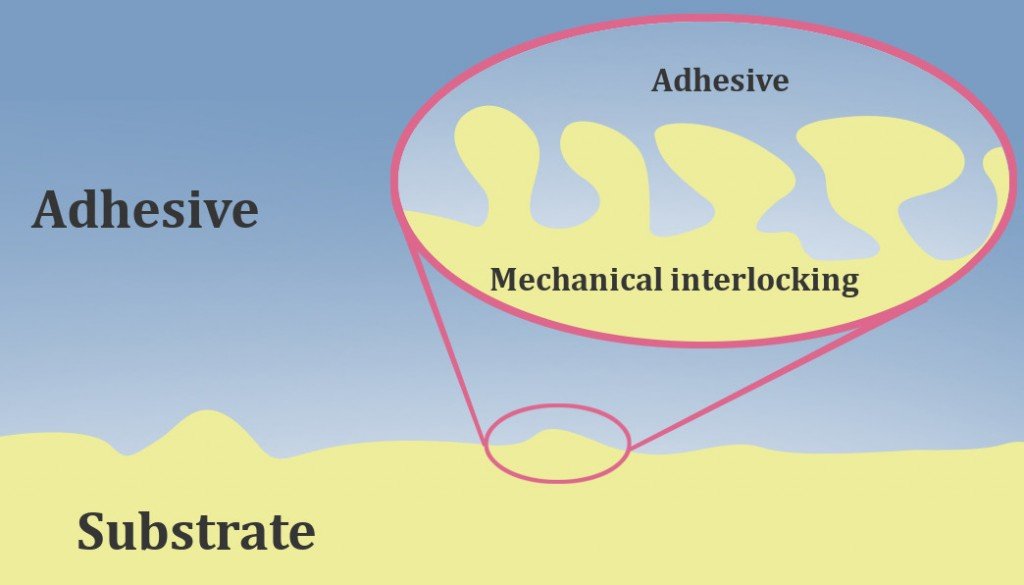
When the glue is inside the bottle, however, there isn’t enough air to interact with the glue,
There simply isn’t enough air to evaporate the solvent present inside the glue. Consequently, the glue doesn’t adhere to the interior surface of the tube. However, if you leave the bottle’s cap off for some time, the glue inside the bottle could dry up and be rendered useless. There’s also the plastic modeling glue, which consists of polystyrene molecules and acetone as the solvent (which evaporates as the glue is squeezed out of its tube).
Also Read: Why Do Liquids Sometimes Run Down The Side Of The Container When They Are Poured Out?
Why Do Cyanoacrylate Glues Tend To Dry Up Within The Tube?
Super glue (the trade name of a popular glue) works a little differently than white glue (and other commonly used glues). Instead of being comprised of polymers, it consists of a chemical known as cyanoacrylate. Cyanoacrylates are a family of strong fast-acting adhesives that have a short shelf life (about one month after being opened). Super glue is believed to be Ethyl cyanoacrylate (ECA).
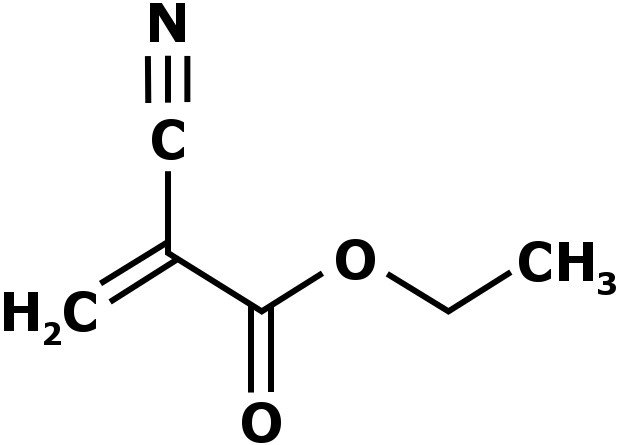
Super glue binds things together when it comes in contact with the water vapor present in the air (more specifically, the hydroxide ions found in water). The moment it comes in contact with water vapor, the cyanoacrylate molecules begin to line up and stiffen, ultimately becoming absolutely hard and solid, providing exceptional adhesion. This is a classic example of chemical adhesion.

That’s why it’s strongly advised to store Super glue in a watertight environment, so that it doesn’t dry up within the bottle itself. On the one hand, we have white glue that needs water to remain non-sticky (within the tube), and on the other, we have super glue, which dries up with even a little exposure to moisture!
How well do you understand the article above!

References (click to expand)
- Cyanoacrylate (Super Glue) Fuming - English202C - www.personal.psu.edu
- Glue and Adhesives - Art Tech - Grand Valley State University. Grand Valley State University
- adhesives-measuring-stickiness : The University of Akron - uakron.edu:80
- Why doesn't Elmer glue stick to its bottle? - UCSB Science Line. The University of California, Santa Barbara
