Table of Contents (click to expand)
It is typically one of four things: either there is an issue with the router, the ISP is using dynamic IP addresses, the router is overheating, or there is overcrowding/interference with the signal.
It has happened to all of us. We’re in the middle of an action-packed movie scene, trying to submit an assignment 5 minutes before the deadline, or are bracing for a critical penalty kick when everything on the screen freezes! That little yellow icon (for a Windows desktop operating systems) says ‘No internet access’ and we feel the chill of doom!

Unless there is some catastrophic failure with the infrastructure setup of your ISP (internet service provider), there is an intuitive fix that we generally try that often works! We head for the router, check the bleeping light on the router, unplug it or switch off the button. We wait a few excruciating seconds and then re-plug it back or switch on the button again. Despite missing those crucial moments of an action-packed movie scene or a high-voltage penalty shootout, you’re at least back online, but why on Earth does it happen in the first place? Particularly when you can’t afford to miss the moment! To alleviate some of that frustration, let’s try to understand some of the science behind Internet disconnection.
Complexity Inside The Router
Although the router may appear to be just a simple box helping you access the Internet, the electronics inside the router are complex. Just like a normal computer, routers have their own CPU, memory, main PCB board, input-output devices, and operating system. All of these things help in managing the data traffic, but these components can get overloaded. Just like you can make your laptop slow down by opening multiple tab browsers, streaming 4K video and playing high-intensity games at the same time, pushing tons of data through multiple devices can similarly impede your router—sometimes causing it to grind to a screeching halt.

Dynamic IP
Complicating the matter even further is that most of the ISPs use what are called dynamic IP addresses. IP addresses are internet protocol, which is like a street address to help the traffic on the internet find your device. ISPs only assign these IP addresses to the devices for a certain period of time. When this period expires, your ISP will assign you a new address. This is the concept of dynamic IPs. Sometimes, due to high data traffic, your router might not be able to connect the new IP address and will continue to look out for the old one, which has already expired. This is tantamount to receiving a parcel to your old apartment, despite having updated the new address!
Also Read: Are We Running Out Of IP Addresses?
Cramped Ventilation And Overheating
Just like any other electronic device, routers are susceptible to heat and their performance decreases when they become overheated. Your router might get overheated if it’s shoved in a cramped corner with the ventilation holes blocked by cables and other stuff in the vicinity. Also, if you don’t clean your router regularly, a lot of dust gathering on it might also block the ventilation holes of the router. Basically, your router needs to breathe to work properly. Make sure it’s not placed in a cramped corner that is overstuffed with cables and other accessories on every side.
Also Read: How Does Dust Affect Your Computer’s Performance?
Overcrowding And Interference
There are certain issues that aren’t necessarily caused by router malfunction. Most home internet connections are on Wi-Fi these days, which essentially operates on airwaves. These airwaves sometimes get overcrowded, especially if Wi-Fi is operating on the common 2.4 GHz frequency band, where noise comes from common household appliances, such as microwave ovens, baby monitors and even signals from other nearby routers. Signals on the same frequency can overlap with each other (called interference), making it difficult for your receiving devices (mobile device or computer) to hear what your router is trying to say (communicate) through the airwaves.
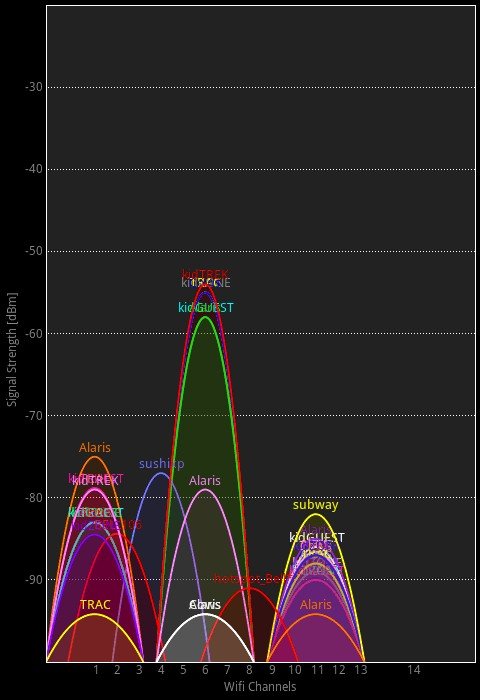
If this is the case, you can go to your router settings and change the channel, or simply try switching from 2.4 GHz to a 5 GHz band, provided your router supports that particular bandwidth.
Also Read: Do Microwaves Interfere With WiFi Signals?
Software Problems
The problem of poor internet connectivity sometimes lies in a buggy software, application or extension.
Running on an obsolete software or a driver can sometimes lead to hiccups in Internet connectivity. Thus, you should make sure that the device you’re using is running on the latest version of the operating system. Sometimes uninstalling and reinstalling Wi-Fi drivers can fix Internet issues.
Interestingly, simply switching browsers may sometimes fix the Internet issue if the problem is not in the router’s hardware or due to airwave interference. This is because many times an extension, plugin or browser bug can choke your Internet access. One way is to switch to a different browser or try incognito mode to check if the Internet resumes working.
Also, if you’re using VPN (virtual private networks) to access blocked torrent sites, it can also mess up your connectivity. If you can access the Internet on other devices properly, or even on other browsers, a VPN plugin is likely to be the culprit for disrupting your smooth Internet connectivity.
How well do you understand the article above!

